
Theoretical framework, also known as a theoretical standpoint, is the foundation of a qualitative study. It guides researchers to analyze data and helps them interpret results. The theoretical framework is a leading idea in a qualitative paper, and it helps shape the research plan.
It is a set of ideas that explain the relationship among variables in a cause-effect relationship. It guides researchers to make inferences about results or answer a research question.
In general, the theoretical framework presents assumptions about relationships among concepts in theory. It is then applied to the study to explain certain phenomena.
A theoretical framework in qualitative studies is usually based on an existing theory or theories. A proposed theoretical framework should be relevant to the study’s goals and objectives.
Theoretical frameworks can be presented in different ways, including visual models or diagrams used to illustrate relationships among concepts.
A theoretical framework is flexible. It can change as the study progresses, depending on the data collected. Researchers then check if their assumptions are correct, refine the framework based on results, or refine it as they go along the way.
A theoretical framework addresses three key questions:
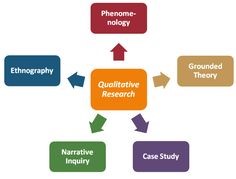
A theoretical framework is a type of theory that links the data and the subject of study.
Some examples of theoretical frameworks in qualitative research are:

This type of inquiry uses emergent theories during data collection and focuses more on discovery rather than explanation.
For example, a researcher might start by asking: “What is the experience of early motherhood like in a particular culture?”
In this case, the grounded theory approach would guide you to collect interviews from mothers and then analyze data inductively to construct theories that emerge from the collected data.
The grounded theory does not try to explain results. It only focuses on describing the phenomenon in question.
Key assumptions of this approach are:
Are you stressed by a qualitative research paper? Worry not! You can hire a research paper writer to help you!
Just follow the simple steps below!
An example of participatory action research for a non-profit organization is to involve community members in the review of policies that affect them.
This framework helps researchers consider power relations within a society and emphasizes how access, voice, and representation are central to a study.
For example, the researcher might ask: “How have the effects of colonization changed the role of women in this culture?”
Here, the critical theory would inform your theoretical framework. This theory helps you explore power dynamics and their relationship to the subject of your study.
The critical theory framework will help you pay attention to the following:
This framework helps you explore the motives behind people’s actions and decisions. It aims to explain why something happens.
For example, the researcher might pose the question: “Why do African-American girls experience emergency room care differently than their Caucasian peers?”
The driving force’s approach would guide you to explore the motives behind people’s actions, which helps you answer this research question.
This approach taps into the following:
This type of inquiry uses symbols and signs to help you understand how people construct meanings. It focuses on the processes through which meaning is influenced by social context.
For instance, the research question could be: “How does this culture define success?”
The semiotic approach helps you explore how symbols are used to construct meaning and how meaning is influenced by cultural context.
Researchers use this framework to determine:
It focuses on subjective experiences, feelings, and thoughts. The goal is to understand the meaning people make of their lived experiences.
For example, the researcher might ask: “What is it like to go blind?”
This inquiry would utilize a phenomenological approach to guide your research process.
This framework seeks to examine:
It is used to explore the “true” or universal aspects of human nature that exist independent of social context. It is a form of philosophical inquiry.
In the example above, the researcher might ask: “Is going blind psychologically devastating?”
This type of framework would help you explore the “fundamental,” universal aspects of human nature. The researcher focuses on broad, conceptual questions about human nature.
This framework helps researchers consider how women are portrayed and treated within society.
An example of a research problem would be: “How does this society define a ‘real man’?”
In this case, the feminist approach would guide you to explore how women are portrayed and treated within society.
According to this framework, the meaning of a situation for an individual is influenced by social interaction.
For example, consider the following research question: “What is a ‘high status’ job in this culture?”
The symbolic interactionist approach would guide you to explore how individuals define and negotiate their status within a culture, which helps you answer this research question.
This approach focuses on how institutions, objects, and behaviors are interconnected within a culture.
For example, the researcher could pose the question: “How does this society keep its history alive?”
The functionalist framework would guide this research question. It helps you explore how institutions, objects, and behaviors are interconnected for this culture.
In this framework, knowledge is fluid, and there are no absolute truths. It challenges traditional concepts of hierarchy, power, and knowledge.
For example, you might pose the question: “How do cultural norms construct gender in this society?”
The postmodern approach would guide you to explore how knowledge is fluid, and there are no absolute truths.
This approach is fluid, so the researcher is free to explore any topic they are interested in. It does not adhere to a specific set of guidelines. Instead, the researcher is free to explore any topic they are interested in.
The researcher is free to pose broad, open-ended questions that focus on the unique characteristics of their study.
This framework looks at how class, race, and gender influence the way people live.
For example, a research question could be: “What is the meaning of ‘success in this culture for a female business executive?”
In this case, the Marxist framework would help you explore how class, race, and gender influence the way people live. This framework would help you consider the unique experiences of a female business executive.
Considering the impact of race, class, and gender on people’s lives within this society would guide your research process.

This approach helps you analyze language and meaning-making systems. It focuses on the process through which social structures are created and maintained.
For instance, if your research study is about the youth’s understanding of their rights, you might ask: “What is considered ‘childhood’ in this culture?”
The constructionist framework would guide you to explore how social structures are created and maintained. This understanding will help you answer the research question.
When using the constructionist framework, your research study is more of a process than a result. The constructionist approach focuses on the process through which social structures are created and maintained. It helps the researcher consider language and meaning-making systems.
The emergent design focuses on collaborative research. It is used when the researcher wants to bring multiple perspectives into their study and has little control over the research process.
An example of a question you could ask is: “What makes a marriage successful?”
In this case, in an emergent design, you would be collaborating with multiple people or participants to answer this question.
Emergent design framework makes it easier for you to invite participants to share their insights and opinions during your study. This approach will help you involve more people in your research process. It also enables you to gain a deeper understanding of a specific topic.
It works by identifying, understanding, and describing the behavior of individuals within a society.
For example, you might develop a research question such as: “How do people in this culture experience illness daily?”
The individualist approach would help you explore the behavior of individuals within the society.
This framework is best used when the researcher needs a deep understanding of an individual’s experience. It is helpful for exploratory research where you are noticing patterns within people’s behavior.
The radical approach is focused on social change and liberation. The research method uses a major research question to engage in a political project.
For example, you might ask: “How does this culture perpetuate inequality?”
In the radical framework/subversive methods, you would engage in a political project to answer the research question.
The main difference between the radical approach and other frameworks is that you must form a major research question for this approach.
Using the radical framework also helps the researcher ensure that people have a voice in their studies.
This approach helps understand and challenge racism through the lens of law. In this framework, you analyze how laws and other societal structures impact people from different backgrounds.
You might ask: “What are the barriers to education for people of color?”
In this case, the critical race approach will help you explore how laws and other societal structures impact people of different backgrounds.
If you are interested in the intersection of law and social justice, this approach may be for you. It helps you understand how the law works and enables you to develop a productive way to challenge racism.